In the realm of musculoskeletal medicine, advancements continue to emerge, offering innovative solutions for conditions that were once challenging to treat. One such advancement is needle hydrodissection, a technique gaining popularity for its effectiveness in treating various musculoskeletal disorders. In this blog post, we delve into what needle hydrodissection entails, how it works, and its potential benefits for certain conditions.
Understanding Needle Hydrodissection
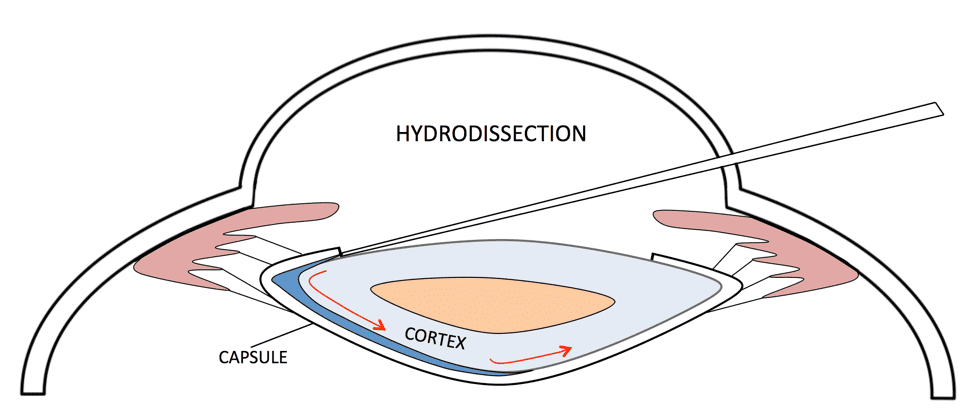
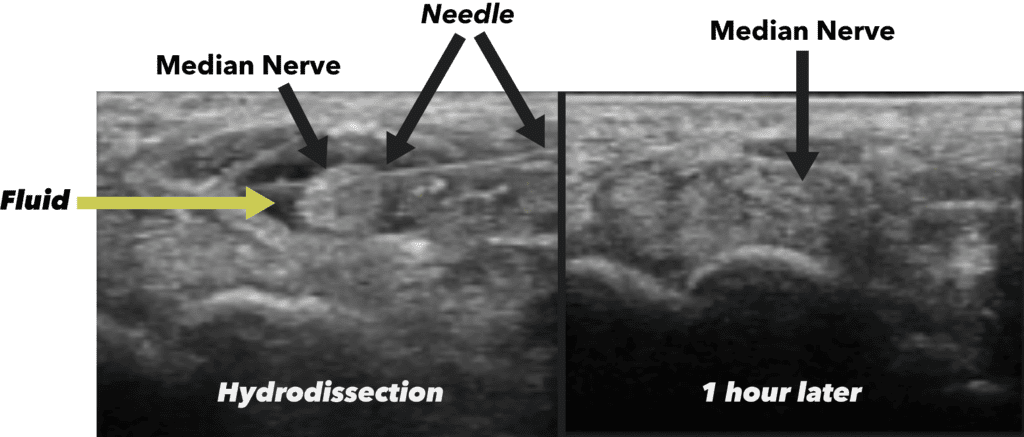
Needle hydrodissection is a minimally invasive procedure that involves injecting a solution, typically a regenerative solution such as platelet growth factors or prolotherapy, but could also be done with a local anesthetic. The solution is injected into specific anatomical regions using a thin needle under ultrasound or fluoroscopic guidance. The goal of this technique is to create a separation between tissues, such as muscles, tendons, ligaments, or nerves, that may be compressed, inflamed, or entrapped due to various pathological conditions.
How It Works
During needle hydrodissection, the injected solution acts as a hydraulic force, causing the targeted tissues to separate. This separation creates space and reduces the pressure on surrounding structures, alleviating pain, improving mobility, and facilitating the body’s natural healing processes. Additionally, the fluid helps to flush out inflammatory mediators and metabolic waste products, promoting tissue healing and regeneration.
Applications in Musculoskeletal Conditions
Needle hydrodissection has shown promising results in the management of several musculoskeletal conditions, including but not limited to:
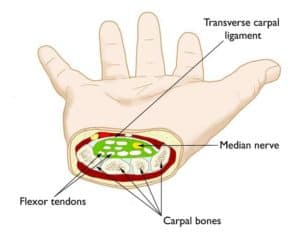
- Entrapment Syndromes: Conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome, and tarsal tunnel syndrome involve compression of nerves within confined anatomical spaces. Needle hydrodissection can help alleviate nerve compression by separating the affected nerve from surrounding tissues, thereby reducing pain and improving nerve function.
- Tendinopathies: Tendinopathies, such as patellar tendonitis (jumper’s knee) and Achilles tendinopathy, are characterized by degenerative changes within tendons, leading to pain and functional impairment. Needle hydrodissection can target the affected tendon, promoting tissue healing and reducing inflammation by creating space and facilitating nutrient delivery to the area.
- Myofascial Pain Syndromes: Myofascial pain syndromes involve trigger points or areas of hyperirritability within muscles, leading to localized pain and restricted movement. Needle hydrodissection can be utilized to inject fluid into these trigger points, disrupting the taut bands of muscle fibers and providing pain relief.
- Joint Conditions: Needle hydrodissection can also be employed in the treatment of certain joint conditions, such as adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder) and osteoarthritis. By creating space and reducing inflammation within the joint capsule, this technique can help improve range of motion and alleviate pain associated with these conditions.
Benefits of Needle Hydrodissection:
- Minimally Invasive: Needle hydrodissection is a minimally invasive procedure that can be performed in an outpatient setting with little to no downtime.
- Targeted Treatment: The ability to precisely target specific anatomical structures under imaging guidance allows for accurate delivery of therapy to the affected area.
- Reduced Risk: Compared to surgical interventions, needle hydrodissection carries minimal risk of complications such as infection, bleeding, or nerve damage.
- Potential for Long-Term Relief: By addressing the underlying pathology and promoting tissue healing, needle hydrodissection may offer long-term relief from musculoskeletal pain and dysfunction.
Needle hydrodissection represents an important tool in comprehensive care for various musculoskeletal conditions, offering a minimally invasive, targeted, and effective treatment option for patients seeking relief from pain and functional impairment. As research in this field continues to evolve, needle hydrodissection holds the potential to revolutionize the way we approach the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders, improving outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for individuals worldwide.