The knee is one of the most important joints in your body in order to continue to do the things we love to do as we age. Unfortunately, the knee is also the most common joint to develop wear and tear, leading to the deterioration of the knee cartilage (arthritis). To ensure long-term joint health, it is a great idea to adopt strategies that promote cartilage maintenance. In this blog, we will explore effective approaches supported by scientific evidence to maintain healthy knee cartilage. Additionally, we will discuss the potential benefits of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy in halting the arthritic process.
Weight Management and Exercise:
- Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing stress on the knee joint and preserving cartilage integrity. Numerous scientific studies, such as Gersing et al.’s research published in Arthritis Care & Research (2017), highlight the association between obesity and knee osteoarthritis (OA). By adopting a diet restrictive in sugars and processed foods as well as engaging in regular exercise, you can effectively manage weight and decrease the risk of cartilage degeneration. Additionally, for every one pound of weight lost in the abdomen you can reduce the stress on the knees by 4 pounds!
Low-Impact Exercises and Muscle Strengthening:
- Regular exercise plays a significant role in maintaining overall joint health. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, or walking, can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee joint without subjecting the cartilage to excessive stress. Strengthening exercises, particularly those targeting the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles, provide stability and support to the knee joint. A study conducted by Kettunen et al. and published in the American Journal of Sports Medicine (2016) showed that regular exercise, combined with muscle strengthening, reduces the risk of knee OA progression.
Avoidance of Repetitive High-Impact Activities to excess:
- Certain activities, such as running, jumping, or high-intensity sports, involve repetitive high-impact movements that can contribute to cartilage breakdown especially if they lead to injury. Scientific research, including a study by Sharma et al. published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research (2017), highlights the correlation between high-impact activities and an increased risk of knee osteoarthritis. However, other studies have actually shown running or jumping to have a protective effect on knee cartilage. The key is to give yourself adequate rest days in between high impact activities and to do your best to avoid injury. If you engage in such activities, ensure adequate rest days, cross-training, and the use of appropriate footwear to minimize the impact on your knee cartilage.
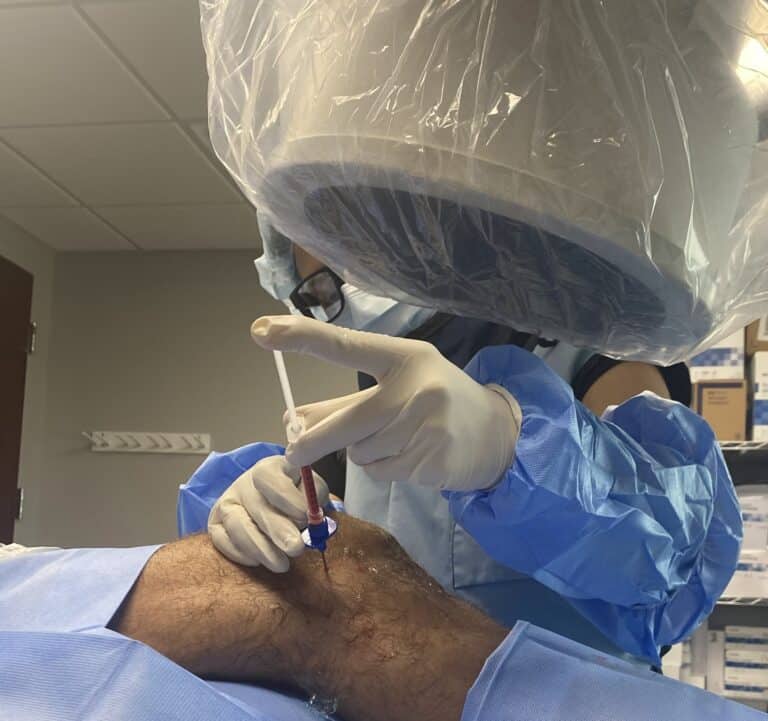
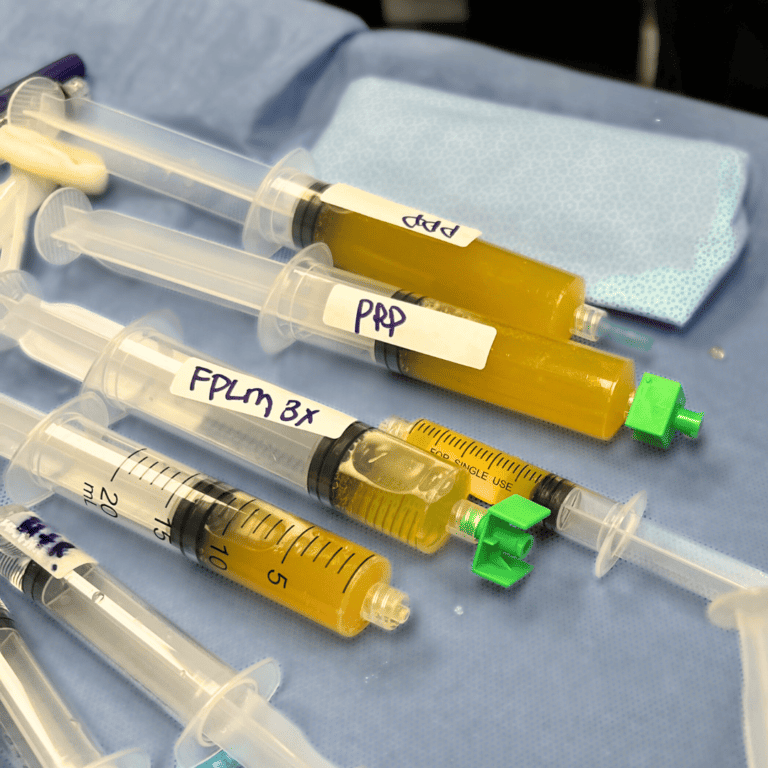
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy has gained attention in the field of regenerative medicine as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis. PRP is derived from a patient’s blood and contains a concentrated amount of platelets, growth factors, and cytokines that aid in tissue regeneration and healing.
Several studies have explored the potential benefits of PRP in reducing the progression of arthritis. A study conducted by Mishra et al. and published in The American Journal of Sports Medicine (2013) demonstrated that PRP injections provided significant pain relief and improved knee function in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
Moreover, PRP has shown promising effects in reducing metalloproteases, which are enzymes responsible for cartilage degradation in arthritic joints. A study by Wei et al. published in Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery (2016) showed that PRP therapy reduced metalloprotease activity, and can potentially halt the arthritic process.
The Takeaway?
These results show great promise for the role that PRP therapy can play in the long term care of cartilage in the knees. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is necessary to determine if PRP therapy is suitable for your specific condition.
Maintaining healthy knee cartilage is crucial for preserving joint function and preventing conditions such as knee osteoarthritis. By incorporating weight management, regular low-impact exercises, muscle strengthening, and considering therapies like PRP patients can give themselves the best chance at preserving their knee cartilage and continuing to do the things they love to do.