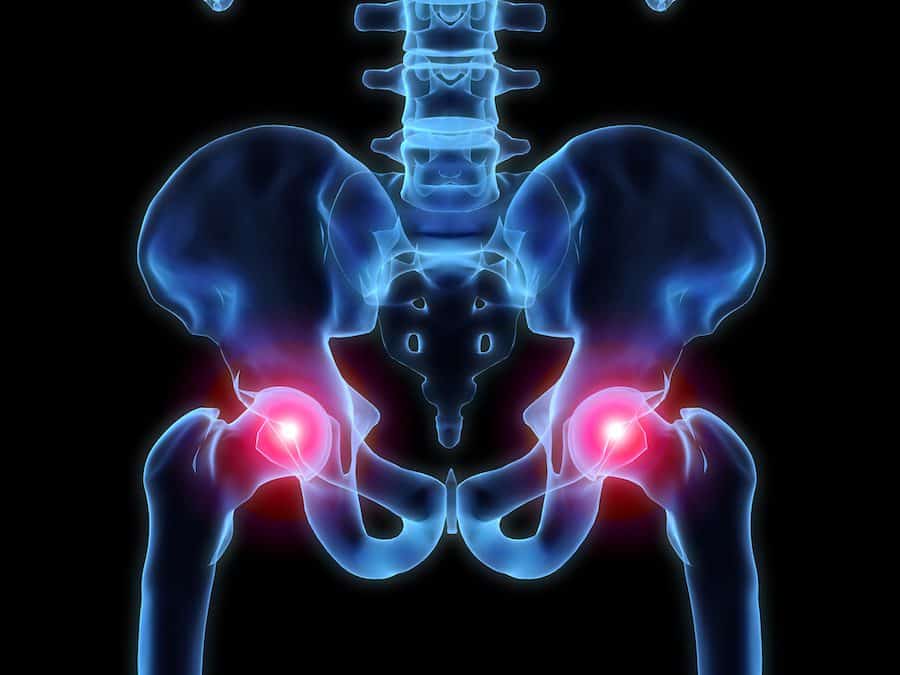
Hip pain is often associated with aging — approximately 14% of adults ages 60 and older experience regular hip pain. It’s often indicative of someone who has lived an active, adventurous lifestyle. For instance, the rate of chronic hip pain doubles to 30% among adults who enjoy sports regularly. Don’t let sore hips stop you from pursuing the life you love. With the right treatment, you can relieve your chronic pain and get back to doing what you love.
Why Does My Hip Hurt? Common Causes of Chronic Hip Pain
Osteoarthritis is the most common cause of chronic hip pain, reports a study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy.
With this degenerative, age-related condition, the cartilage surrounding the hip joints wears down over time. Without the protective cartilage there, and as the joint space narrows, bone spurs may develop, leading to pain that gets worse over time.
Degenerative arthritis may be triggering your hip pain if you experience symptoms like:
- Stiffness or a “locking” sensation in your hip that makes it hard and painful for you to walk.
- Increased pain in the morning, after periods of inactivity, or during strenuous exercise.
- Pain that starts in your groin area and spreads outward to your knee and butt.
- Decrease in your range of motion leading to difficulty with normally simple activities such as: putting on your pants and cutting or painting your toenails.
Other common causes of hip pain include:
- Tears or injuries to your hip labrum (the lining in your hip socket similar to a meniscus in the knee)
- Tears or degeneration of the tendons around the hip, for example: the hamstring tendon at the back of the hip, abductor cuff (gluteus medius and minimus tendons) at the side of the hip
- Trochanteric bursitis caused by inflammation at the side of the hip, often triggered by overuse, poor posture or an injury (and often associated with abductor cuff injuries)
- Hip fractures
- Osteonecrosis (poor bone health caused by poor blood circulation)
How Does Hip Pain Get Diagnosed?
The longer you wait to treat your hip pain, the worse it can get, and the harder it may be to treat.
An early diagnosis and intervention is critical. Your doctor will start with a physical examination, where he will assess factors like the way you walk, your range of motion, and how you react when different forms of pressure are placed on your hip.
Your doctor may also order imaging tests, such as an MRI scan, a CT scan, or an X-ray to get a better look at the health of your hip. And if trained adequately, your doctor may be able to administer a highly technical and informative diagnostic ultrasound exam at the time of your consultation.
Is Surgery the Best Option for Treating Hip Pain?
Non-surgical interventions are generally preferred. In fact, Harvard Medical School warns that surgery should be the last resort for treating a joint condition like hip pain.
There are many significant drawbacks to hip surgery:
- Some patients report little to no improvement after undergoing surgery.
- Others experienced numerous complications after having a hip operation, such as lower back pain, stroke, and heart attacks.
- Many people have an allergic reaction to the materials used in hip replacement surgery.
- And even if you don’t experience such complications, many hip replacements don’t last much longer than 10 years.
Instead, your doctor may suggest a variety of non-surgical approaches to effectively relieve your hip pain:
- Lifestyle modifications including dietary changes, weight loss, and certain exercises guided initially by a physical therapist can help reduce the wear and tear on your joints, slowing the degenerative breakdown of your hip cartilage.
- Visiting a massage therapist, physical therapist, and acupuncturist can help to reduce or even eliminate hip pain.
- Reducing inflammation: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help, especially if your hip pain is due to arthritis. However, these medications carry significant risk of creating other systemic issues if used more than in small amounts intermittently. Other natural anti-inflammatory foods and supplements include turmeric/curcumin and omega-3 fatty acids can be beneficial as well as other supplements such as Glucosamine/Chondrotin.
- Narcotics are an option but ongoing use is generally discouraged.
- Steroid/Cortisone injections can help alleviate the acute pain for a short time but also are generally discouraged due to the deleterious effects on the cartilage and bones and other systemic issues than can occur (increased blood sugar, increased risk of infection, delay of wound healing, increased risk of cataracts, etc.).
If these approaches don’t provide relief, more and more people are turning to advanced interventional orthopedics to heal your hip joint. In fact, this option may be the best first approach to treating the hip condition.
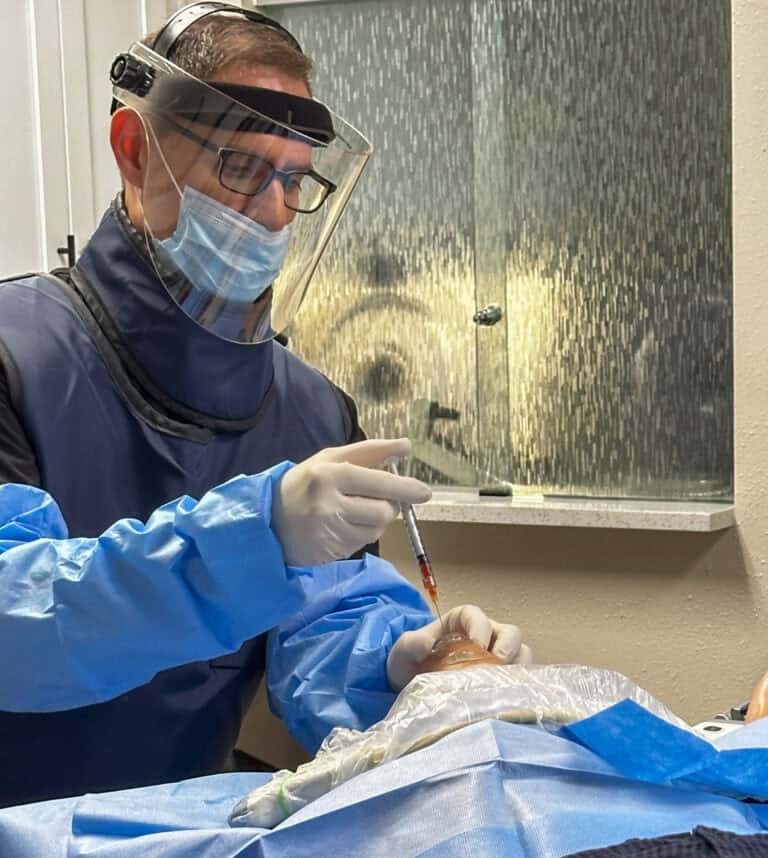
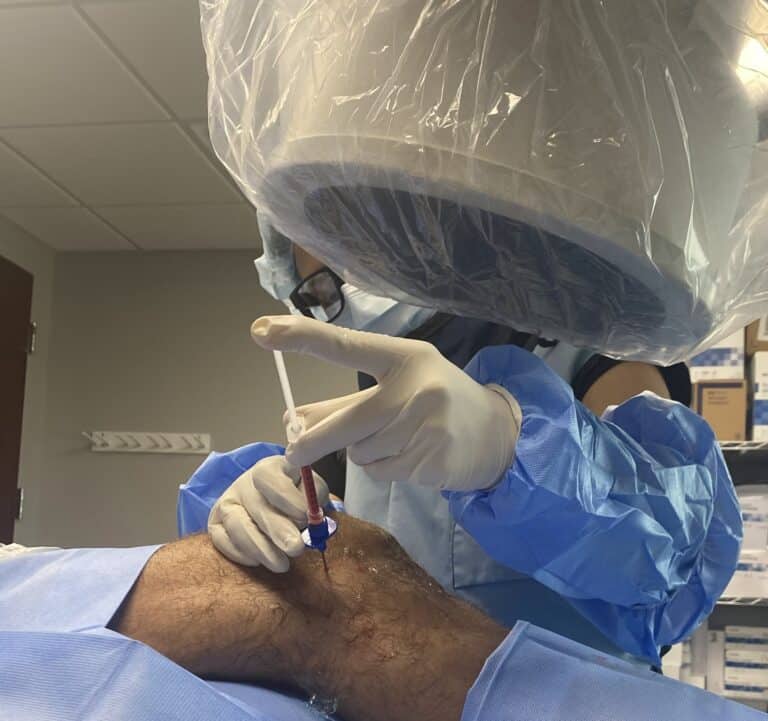
Instead of harmful steroid injections, NSAIDs, narcotics, or invasive hip surgeries, the Regenexx family of treatments uses highly skilled ultrasound and X-ray guided imagery to precisely place your body’s own healing agents (i.e. blood platelets, bone marrow concentrate, and other orthobiologic products that come from you) into your hip joint and other damaged or weakened structures.
These treatments help reverse or stop the degenerative process naturally, effectively, and quickly. The process triggers your body to strengthen and heal damaged tissue in your hip joint, as well as decrease inflammation, helping to reduce hip pain, improve hip range of motion, and restore hip functioning without any surgery required!
Beware of providers offering to use “younger stem cells.” This is an organized crime scam. It is illegal to use stem cells from someone else in your body without getting FDA drug approval first. Furthermore, it has been found that the “products” sold to unwitting providers, do not actually have any living cells in them.
The effects of highly skilled, FDA-compliant orthobiologic injections are wide-reaching. Bone marrow stem cell and blood platelet procedures can address hip pain and dysfunction from a wide array of different conditions by improving stability, strengthening weakened tissue, and decreasing inflammation in the long term.
Contact us today to learn how advanced interventional orthobiologic injections using superior lab techniques and highly skilled image-guided procedures can address your hip pain without the drawbacks, complications, and difficulties of undergoing traditional hip surgery or the risks associated with NSAIDs, narcotics, or cortisone.